

BDX100
Structure and Composition
BDX100 is a preparation of outer membrane protein (OMP) non-covalently complexed to lipopolysaccharide (LPS). OMP are proteinaceous nanoparticles derived from the Gram-negative bacterium, Neisseria meningitidis, consisting primarily porin Classes 1, 2, 4 & Lip. LPS is purified from the outer membranes of Shigella flexneri. The ratio of protein to LPS in Protollin is approximately one to one. BDX100 is commonly called Protollin.
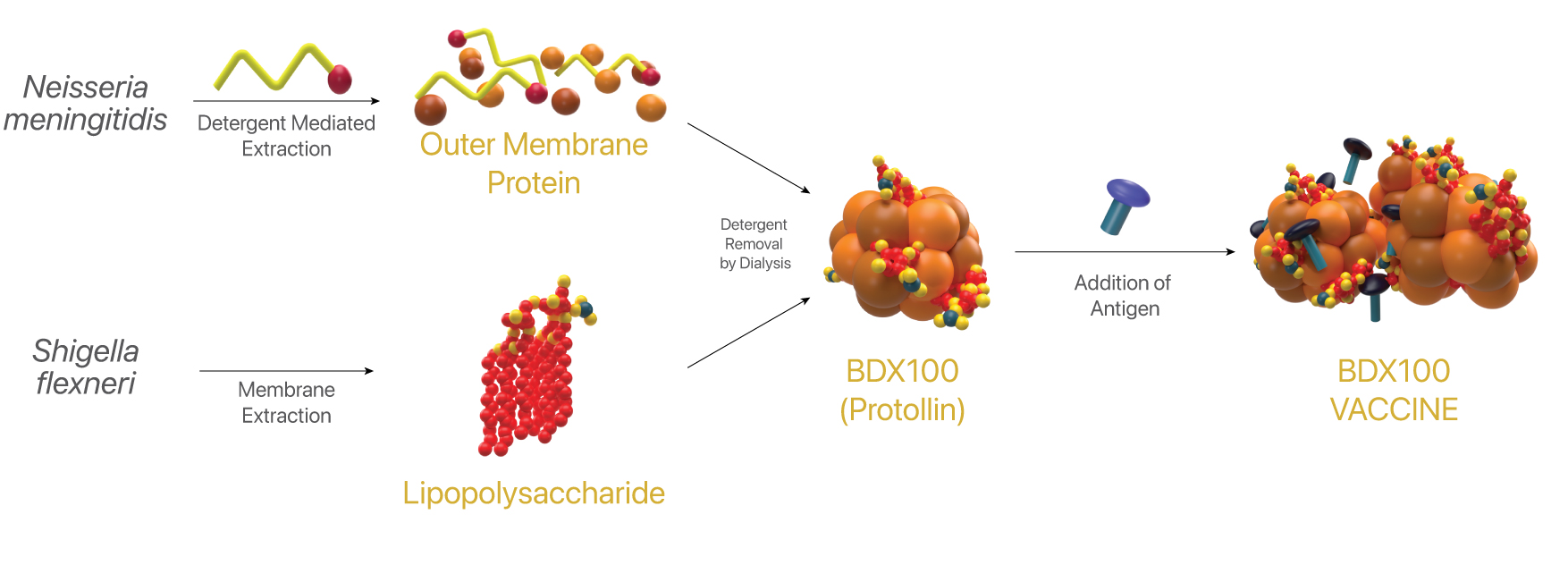
Mechanism
TLR 1-2 and TLR-4 agonist. MyD88 dependent. Meningococcal OMPs engage multiple toll-like receptors. Protollin is believed to associate non-covalently with hydrophobic domains in amphophilic antigens for presentation to the mucosal immune system. BDX100 also acts directly on the innate immune system independently of an antigen.
Multiple agonists. TLR1-2 & TLR4 involvement demonstrated by NF-κB activation in TLR1-2 and TLR4 transfected HEK cell lines. BDX100 activated NF-κB in a concentration dependent manner. CD14 receptor involvement has been demonstrated in human cells. BDX100 adjuvant effect on flu immunization (IgG) is reduced in MyD88, but not TLR2, knock-out mutants of C57BL/6 mice. Studies using LOS hypo-responsive mice (C3H/HeJ) suggest that TLR4 contributes to the antibody response elicited by BDX100-influenza vaccine. Studies with TLR2 knock-out mutants of C57BL/6 mice show BDX100 induced increases in mucosal uptake in Peyer’s patches in mice and BDX100 induced migration of dendritic cells into the follicle-associated epithelium to both be TLR2 dependent.
Cell Types and Tissues Targeted by BDX100
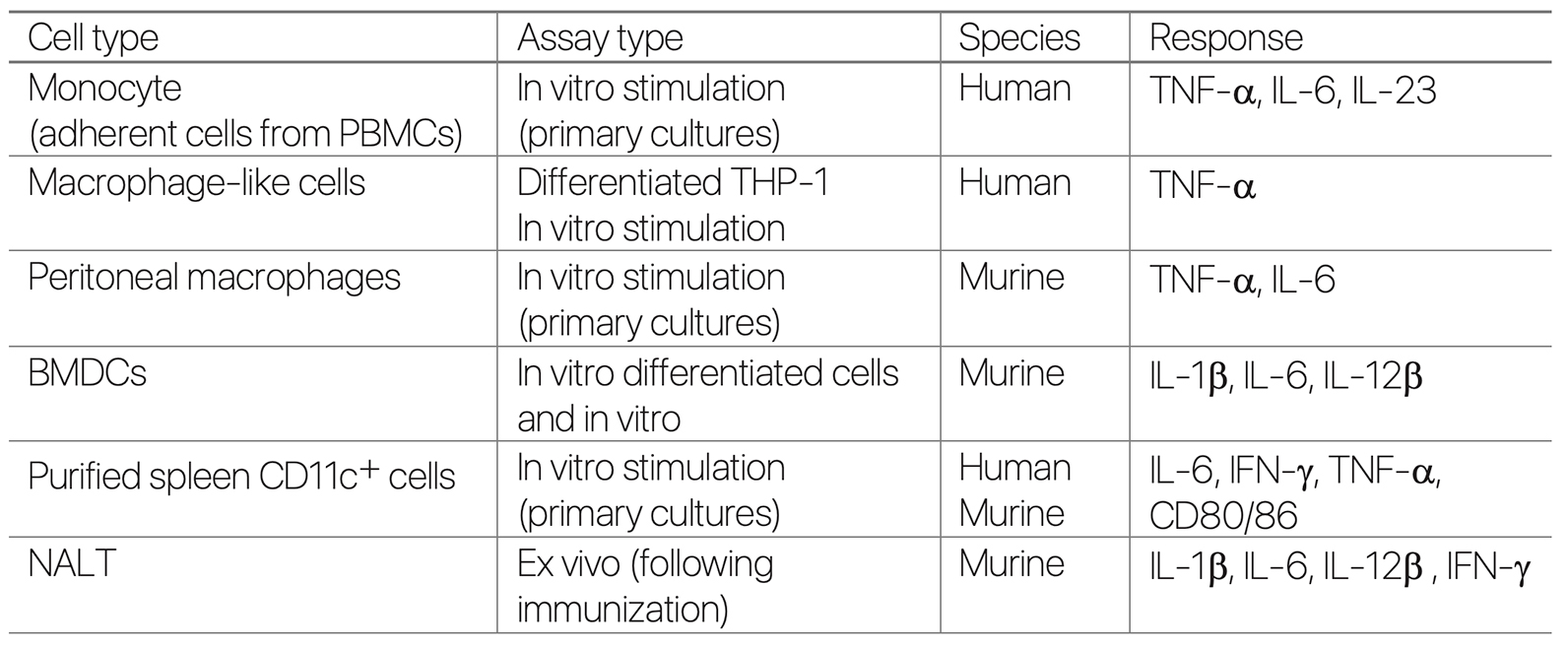
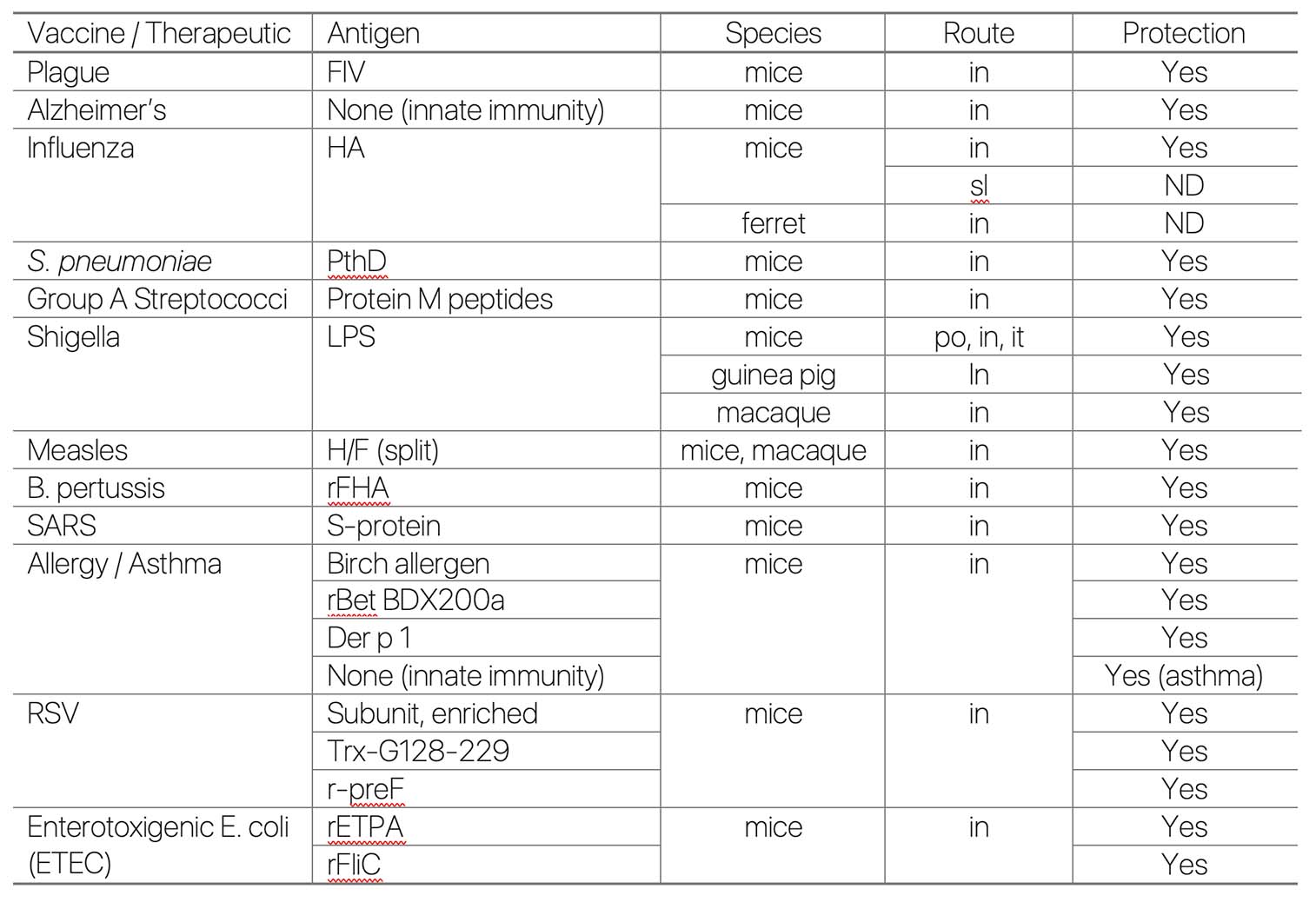
Summary of Preclinical Studies
Safety
Two toxicology studies were conducted as part of the shigellosis program, one examining BDX200 with Shigella sonnei LPS, the second for BDX200 complexed to Shigella flexneri LPS. Both studies revealed no unexpected findings. More recently, one GLP repeat dose toxicology study was conducted (1, 2 and 4 doses at 2 week intervals) as part of the nasal plague vaccine program. Protollin (12 mcg), with and without the FIV antigen, showed no unexpected findings following intranasal administration in BALB/c mice. CNS distribution study showed no translocation of Protollin to olfactory bulb following intranasal administration in mice.
No damage was detected to the blood brain barrier (fibrinogen test) in either the hippocampus or olfactory bulb. No Protollin was found in the brain olfactory bulb.
After 8 months of weekly treatment:
Mobility assessment by open field testing, an index of locomotor/exploratory activity and anxiety, showed no impairment.